A Dense Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Analysis for Bioenergy-Related Traits in Sweet Sorghum
Global warming, climate change, and energy security issues make sustainable biofuels superior to conventional fossil fuels, as a source of energy. Sweet sorghum’s [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] water-use efficiency, heat and drought resistance, and high yield, make it a preferred choice as a biofuel crop. Improving bioenergy-related traits in sweet sorghum has a direct effect on bioethanol production. In an effort to understand the genetic basis of relevant traits, scientists from Akdeniz University, West Mediterranean Agricultural Research Institute, and Sabanci University generated an F2 population by crossing sweet sorghum cv. ‘Erdurmus,’ which is high-sugar yielding, and grain sorghum cv. ‘Ogretmenoglu,’ which is low-sugar yielding. The researchers used double digest restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (ddRAD-seq) for SNP discovery to construct a genetic map of the F2 population. Although ddRAD-seq had never before been used to create a genetic map in sorghum, the authors found that the linkage map to be of similar length to those published in previous research, but the marker distribution and density were improved.
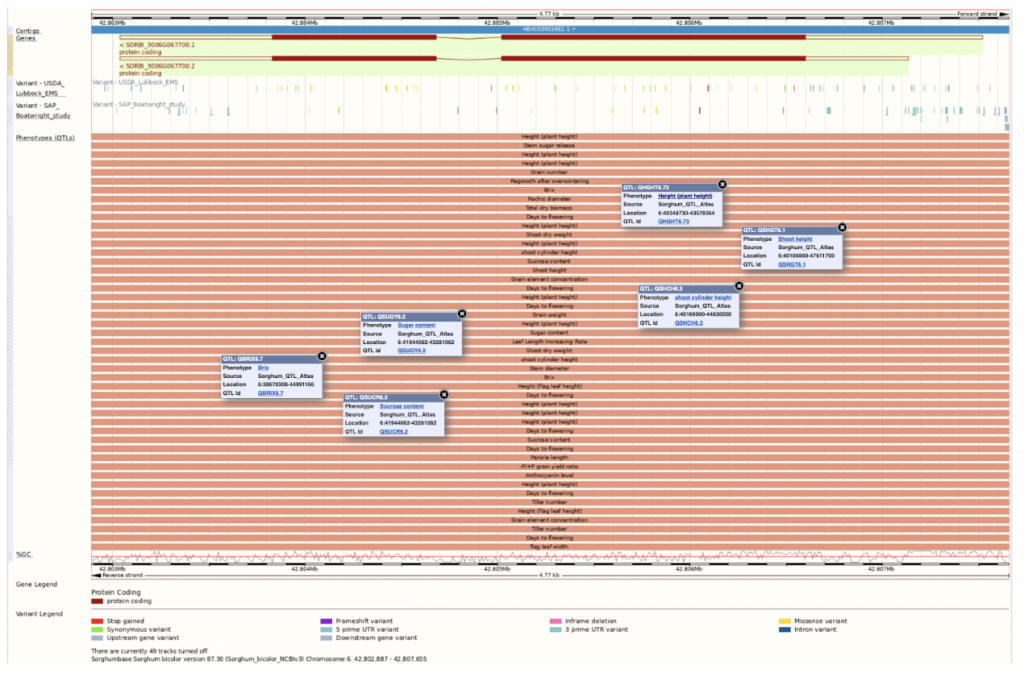
F3 lines were produced from each F2 individual and grown in two environments, including lowland and highland sites, and phenotypically assessed for bioenergy-related traits. To analyze their genotypes, SNP markers were used to identify bioenergy-related QTLs; ten QTLs associated with plant height, Brix, fresh biomass weight, and plant juice were identified. Future work can harness these QTLs and molecular markers to develop elite sorghum lines for bioenergy production.
SorghumBase Example:
Reference:
Guden B, Yol E, Erdurmus C, Lucas SJ, Uzun B. Construction of a high-density genetic linkage map and QTL mapping for bioenergy-related traits in sweet sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 5;14:1081931. PMID: 37342135. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1081931. Read more


