A Sequence-Indexed Sorghum Mutant Population for Crop Functional Genomics
Sorghum bicolor, with its compact genome structure and high heat and drought tolerance, is an excellent model for functional genomics studies in C4 crops. Mutant resources have been widely used in plants to understand gene functions. Researchers from Texas Tech University, USDA-ARS, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory published the sequencing of 1,000 randomly selected ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS)-induced sorghum mutants that covered 98% of sorghum genes.
Additionally, out of the 9 million mutations, 610,320 mutations were identified in the promoter and enhancer regions of 18,000 and 11,790 genes, respectively. This provides a rich resource to study the functions of cis-regulatory elements. Based on the Ka/Ks value, the mutant library experienced little selection (Ka/Ks ~1) in contrast to the sorghum association panel (SAP), which has been strongly selected through breeding (Ka/Ks 0.40). The combined sequencing data from the mutant library and SAP provide powerful tools to study gene mutations and the influence of selection.
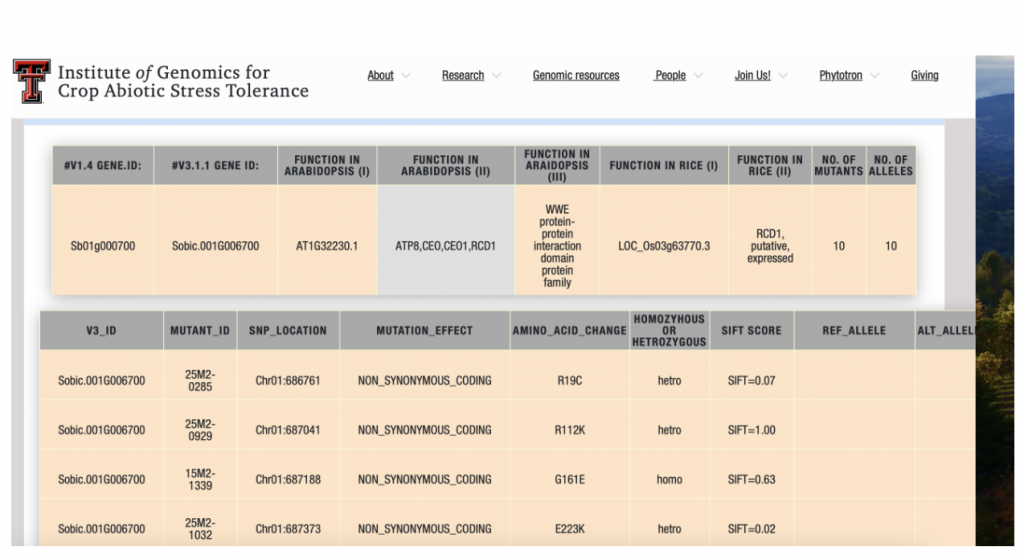
Our sequence-indexed sorghum mutant population offers an excellent platform to discover gene functions in the grass family, supporting plant biology research and crop breeding. Mutations in genes of interest can be searched online through SorghumBase https://www.sorghumbase.org or SorbMutDB https://www.depts.ttu.edu/igcast/SorbMutDB.php.
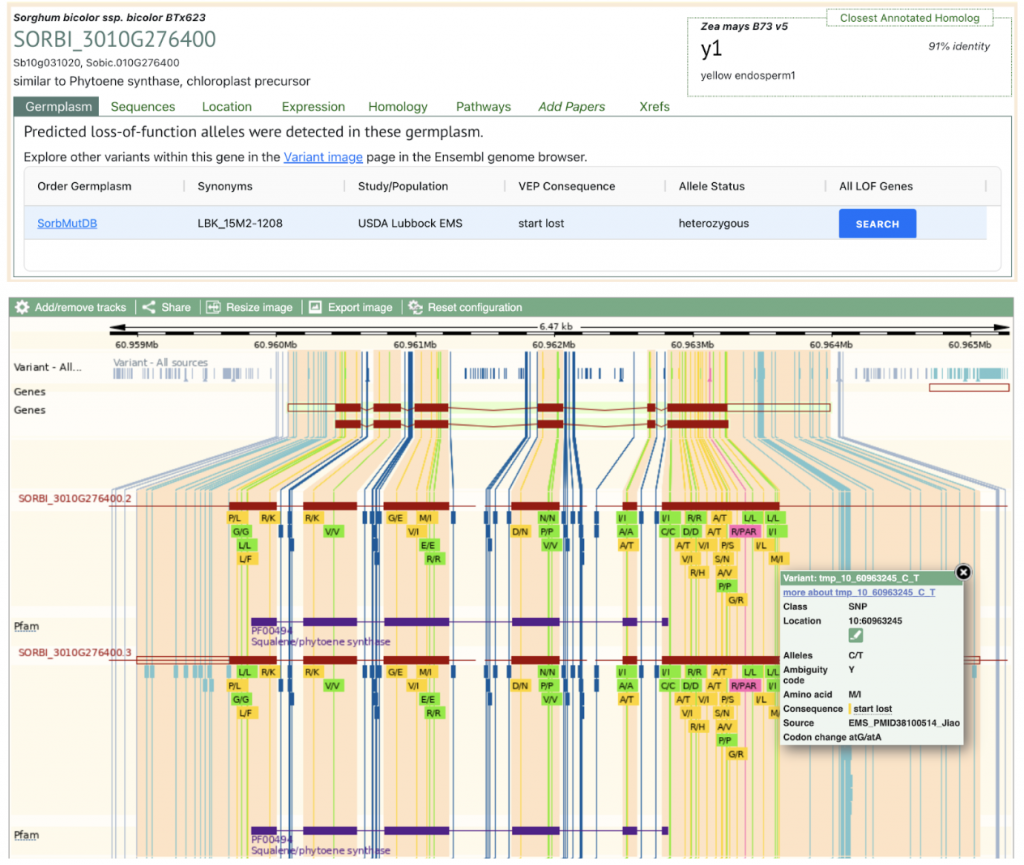
SorghumBase example:
Reference:
Jiao Y, Nigam D, Barry K, Daum C, Yoshinaga Y, Lipzen A, Khan A, Parasa SP, Wei S, Lu Z, Tello-Ruiz MK, Dhiman P, Burow G, Hayes C, Chen J, Brandizzi F, Mortimer J, Ware D, Xin Z. A large sequenced mutant library – valuable reverse genetic resource that covers 98% of sorghum genes. Plant J. 2024 Mar;117(5):1543-1557. PMID: 38100514. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16582. Read more
Related Project Websites:
Jiao Lab at Texas Tech University: https://www.depts.ttu.edu/igcast/Staff/jiao_lab.php